SCALP
Scintillating ionization Chamber for ALPha particle detection in neutron induced reactions
Nuclear data
Since 2014, the group has been interested in determining the effective cross section of the 16O(n, alpha)13C reaction that could be measured on the future NFS facility at SPIRAL2. This reaction is of interest for reactors using water as coolant and moderator, as well as for reactors using oxide fuels. This reaction is responsible for 25% of the helium production and its lack of knowledge (discrepancies of up to more than 30% are observed in existing data, including the most recent ones) leads to an uncertainty of 7% on this production (for PWRs) and an uncertainty of 100 pcm on the determination of the keff (for PWRs, RNR). In the framework of the NEA HRPL a determination of this cross section at better than 5% of the energy threshold (2.36 MeV) up to 20 MeV is required since 2005. This request is based on the conclusions of NEA/WPEC No. 26 and was reinforced in 2014 by the work of the CIELO1 group (NEA/WPEC No. 40).
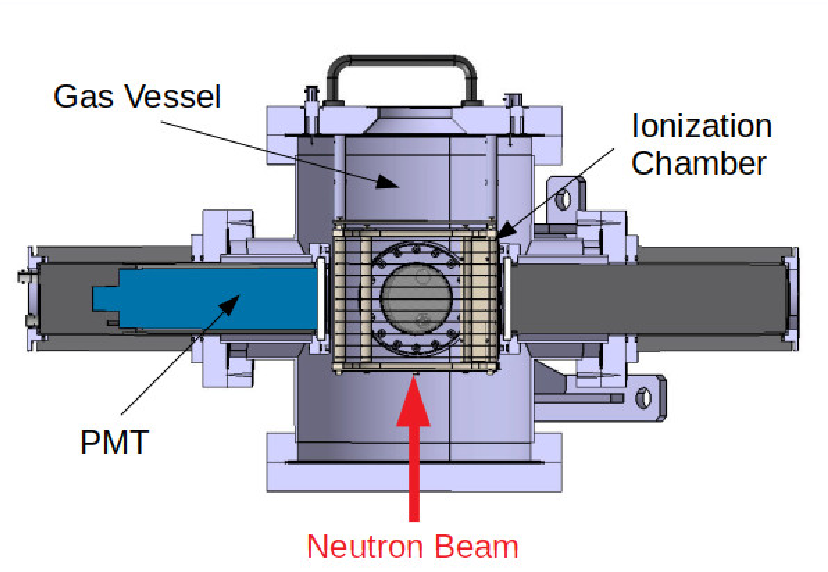
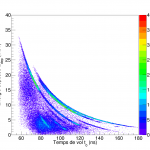
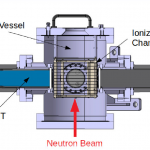
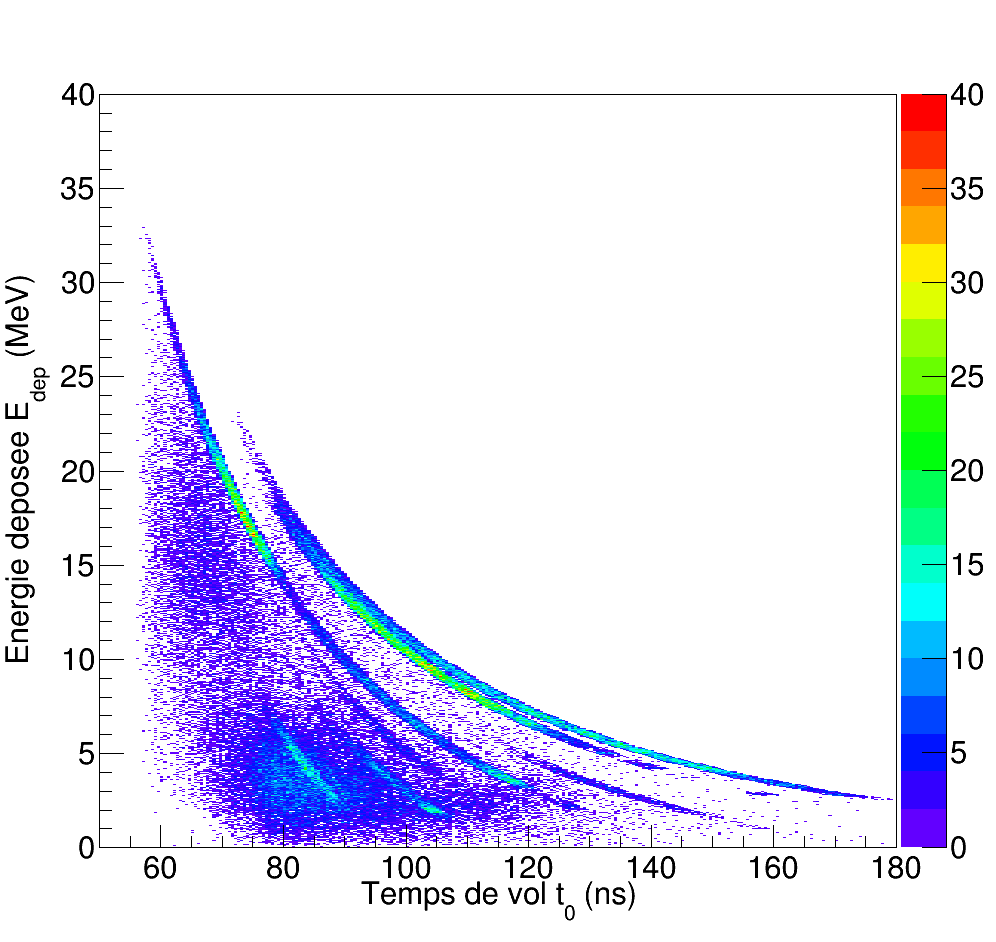
To realize the measurement of this cross section, the SCALP device has been studied and developed at LPC Caen. The device consists of a scintillating ionization chamber filled with a mixture of CF4, chosen for its scintillating properties, and CO2 whose oxygen is used as target nucleus. It allows, on the one hand, to measure the energy deposited in the ionization chamber (chio) and, on the other hand, to determine the energy of the incident neutron using the time-of-flight method and the fast signal associated with the scintillation process. The combination of the energy deposited in the chio by the produced particles with the neutron energy allows to discriminate and select, among all the reactions taking place in the gas, the nuclear reaction of interest. The characteristics of this mixture for different CO2 concentrations have been studied in the laboratory with alpha sources.
In order to estimate the performances of our detector and to study the reactions (n, alpha) with 12C and 19F, the strategy followed consists in carrying out a first measurement campaign with CF4 alone, at different neutron beam facilities in Europe: the GENESIS platform (LPSC, Grenoble, France), the nELBE (HZDR, Dresden, Germany) and GELINA (JRC-IRMM, Geel, Belgium) facilities. A second campaign will be performed with CF4 and CO2 to estimate the performance with a gas mixture, in particular the degradation of the deposited energy and the time-of-flight resolution.
As the 16O(n, alpha) reaction rates will be too low to reach the targeted uncertainties using the nELBE or GELINA facilities, a new experimental campaign will be performed at the NFS facility of SPIRAL2 (Ganil, France). NFS will provide the neutron intensity to meet the HPRL requirements.
The last step of the SCALP project will be to produce the data files of the effective cross sections (n, alpha) on the 16O and 19F nuclei, to make these data available on the EXFOR platform and to propose a new evaluation of the 16O (n,alpha) effective cross section in collaboration with the evaluation community.
The SCALP project is supported by:
the SANDA project (H2020 SANDA GA 847552), WP2 “New nuclear data measurements for energy and non-energy applications”, Task 2.1.2: “Neutron induced charged particle production cross sections.
the ARIEL project (H2020 ARIEL GA), financial support of the experiment at the nELBE facility.
the Master project IN2P3 OPALE, “des dOnnées exPérimentAles à l’évaLuation pour les réactEurs”.
the research program NEEDS of the CNRS via the project NACRE, WP1 Effective section, Action 1.2 Study of the reaction 16O(n, alpha)13C.